The “summer solstice” occurring on June 21, marks the “longest day of the year” and signifies the onset of summer in the northern hemisphere. It marks a change in seasons, and closer to the North Pole, the duration of the day extends significantly. However, this does not imply that Earth moves closer to the Sun during this time. In fact, during the summer solstice, Earth’s orbit positions it farther from the Sun.
As you move closer to the North Pole, the daylight hours become longer during summer solstice. For example, residents in the UK experience an average of 16 hours of daylight, while those living in the Shetland Islands in Scotland enjoy around 19 hours of daylight, according to Royal Meteorological Society.
Why is June 21 longest day of the year?
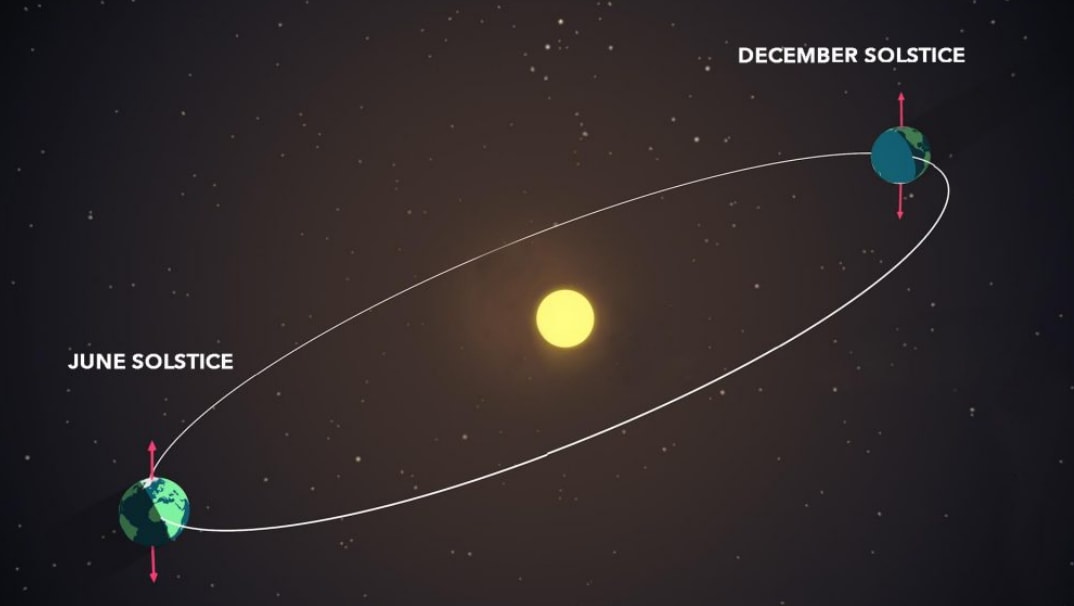
The changing seasons on Earth are a result of its tilted axis, according to NASA. This tilt causes different regions to receive the Sun’s rays at varying angles throughout the year. When the North Pole tilts towards the Sun, it signifies summer in the Northern Hemisphere, while the South Pole tilting towards the Sun indicates winter in the Northern Hemisphere.
During the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted directly towards the Sun, resulting in the “maximum intensity of sunlight and consequently the longest day of the year”.
What does Solstice mean?
The term “solstice” originates from Latin and translates to “sun stands still”, according to NASA. This is because during the solstice, the sunrise and sunset positions are at their extreme points of the year: the farthest northeast for sunrise and the farthest northwest for sunset.
Solstices occur twice annually. In the Northern Hemisphere, the summer solstice takes place around June 20-21, while the winter solstice occurs around December 21-22. During the solstice, the Sun’s path appears to be at its farthest north or south, depending on the hemisphere.
What happens when there is Summer Solstice?
During the summer solstice, at the North Pole, the sun remains above the horizon throughout the day, resulting in a complete absence of sunset. Conversely, in the Southern Hemisphere, which coincides with its winter solstice on the same day, a contrasting scenario unfolds. At the South Pole, the sun does not rise, creating a day devoid of sunlight.
Cultures recognise Summer Solstice
Ancient cultures possessed knowledge of the Sun’s regular seasonal shifts in its path across the sky, the duration of daylight, and the specific positions of sunrise and sunset. Moreover, they constructed notable monuments such as Stonehenge in England and the Torreon in Machu Picchu, Peru, to track the Sun’s yearly progression and anticipate its movements.


